Clone and Experiment with Requests
Use Clone Request to turn any finished trace into an isolated Experiment, so you can safely try new prompts, models, and parameters without touching the original run.
This is the fastest way to A/B test ideas, compare models, and iterate on prompts directly from your existing traces.
What are Clone Request and Experiment?
- Clone Request: the action of taking a finished trace and creating an Experiment from it.
- Experiment: the editable copy of the original LLM request (messages, tools, model, temperature, max tokens, etc.) that you can rerun and tweak independently of the original trace.
How to Clone a Request
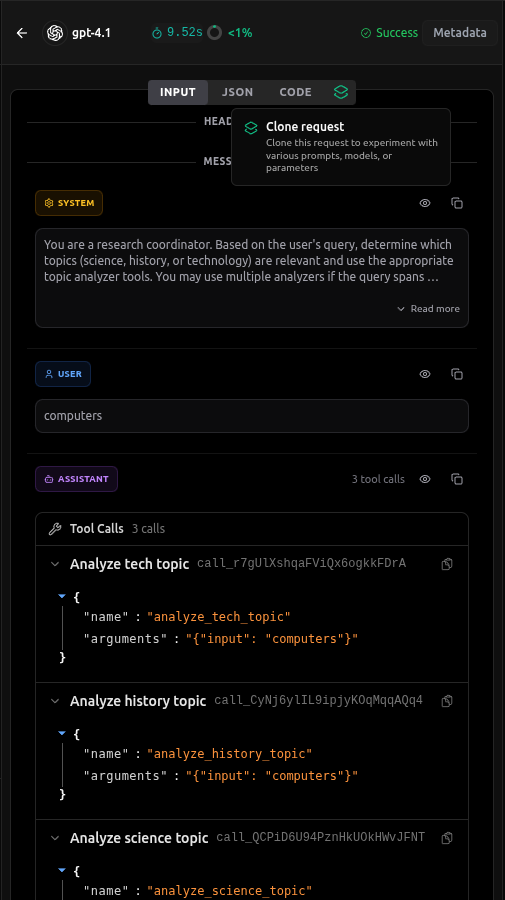
- Open Traces and select a request: In the vLLora UI at
http://localhost:9091, go to the Traces view and click the specific trace (span) you want to clone and experiment with. This opens the Experiment view for that request. - Create the clone: Click the Clone tab/button. vLLora creates a new experiment based on that trace while keeping the original trace and output frozen on the right as Original Output.
The new experiment becomes your New Output area where you can safely change the request and re‑run it as many times as you like.
Editing the Cloned Request
The cloned request is a full OpenAI‑compatible payload with the same messages, tools, model, and parameters as the original. You can edit it in two main ways:
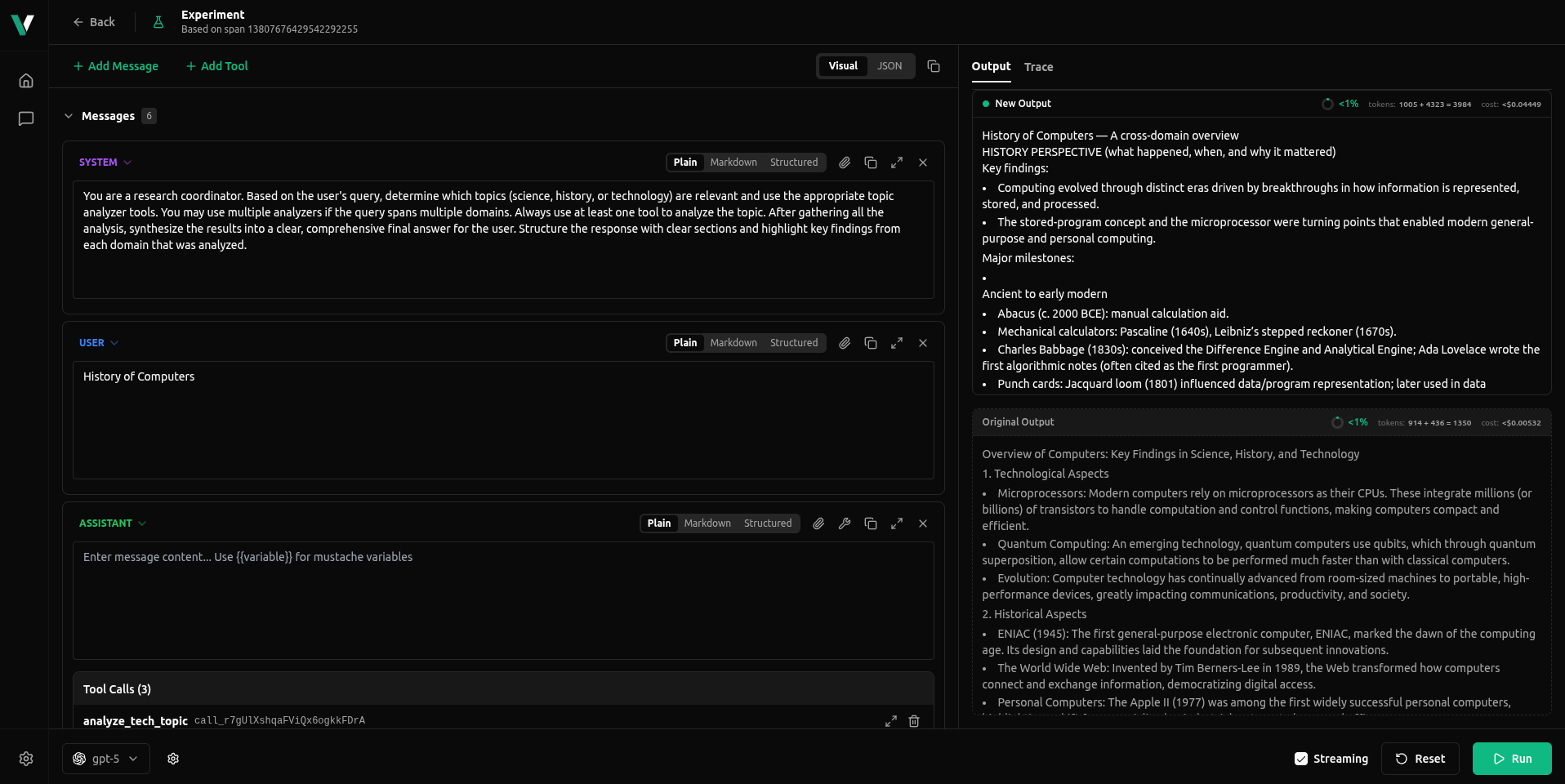
- Visual mode (
INPUTtab)- Edit system and user messages in a structured, form-like UI.
- Add or remove messages, tools, and tool calls to change how the assistant behaves.
- Switch the model used for the Experiment to compare behaviour across providers or versions.
- Great when you want to tweak prompts or tool wiring without touching raw JSON.
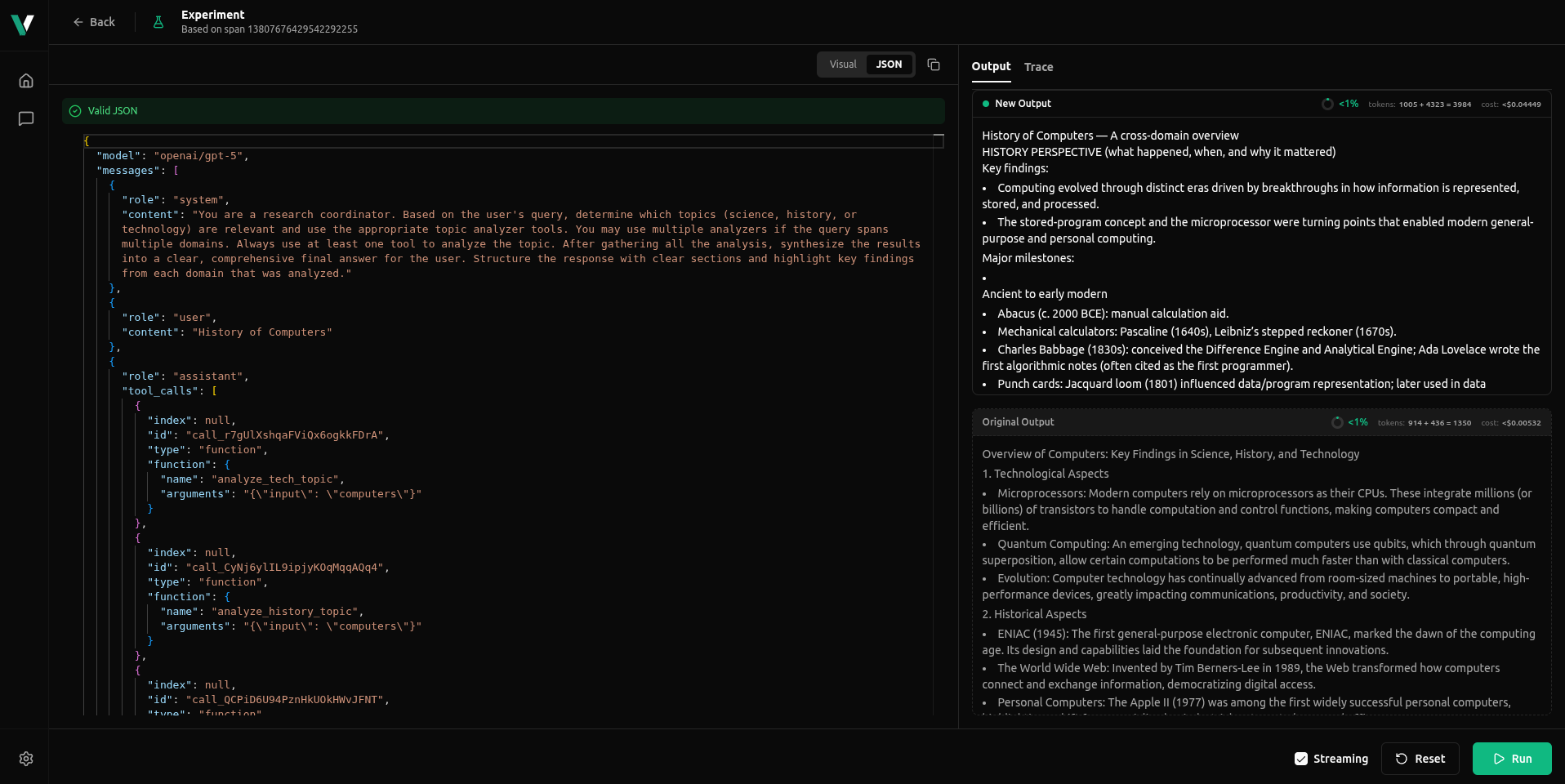
- JSON mode (
JSONtab)- Edit the raw request body exactly as your app would send it.
- Change fields like
model,temperature,max_tokens,tools,tool_choice, and other advanced options. - Ideal for precise parameter tuning or reproducing a request from your own code.
When you’re ready, click Run. Each run of the cloned Experiment creates a new trace, so you can A/B test and iterate freely without ever mutating the original request.
In the Output panel you can compare the cloned Experiment’s New Output against the Original Output at a glance:
- Tokens & context: see how many prompt + completion tokens were used.
- Cost: compare the estimated cost of the original vs the experiment (and how much higher/lower it is, e.g.
<1%). - Trace: every run appears as its own trace in the Traces view, tagged as an Experiment, so you can quickly spot and inspect all your experimental runs and dive deeper into timing, tool calls, and other details.
Use Cases
1. Prompt Engineering
Test different phrasings, instructions, or prompt structures to find the most effective version:
Original: "Summarize this article"
Cloned & Modified: "Provide a concise 3-sentence summary of the key points in this article"
2. Model Comparison
Compare how different models handle the same request:
- Clone a request that used
openai/gpt-4o-mini - Change the model to
anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet - Compare outputs side-by-side
3. Parameter Tuning
Experiment with different parameter values to optimize performance:
- Temperature: Adjust creativity vs. consistency (0.0 to 2.0)
- Max Tokens: Control response length
- Top P: Fine-tune sampling behavior
- Frequency Penalty: Reduce repetition
4. A/B Testing
Create multiple clones of the same request with different configurations to systematically test which approach works best for your use case.
5. Iterative Debugging
When debugging agent behavior:
- Clone a request that produced unexpected results
- Modify specific parameters or prompts
- Test the changes without affecting the original trace
- Compare results to understand what caused the issue
The Clone Request feature makes it easy to experiment and optimize your AI agent interactions without losing your original requests. Use it to refine prompts, compare models, and fine-tune parameters until you achieve the best results for your use case.